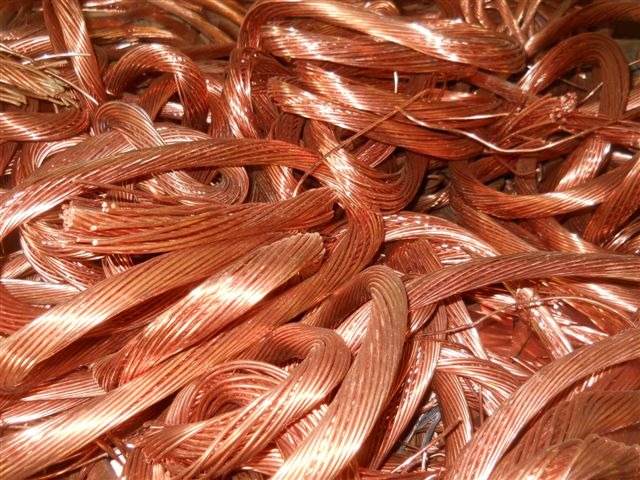
Extraction of Copper Through Froth Floatation Method
Posted on Feb 2, 2019
Copper is one of the most valuable and commonly used metals. Obtaining this metal from its ore is a process referred to as Copper extraction. Copper conversion needs to undergo a series of processes like physical, chemical and elector-chemical processes. These methods have undergone a lot of changes and the processes also vary with region to region. It will hugely depend on source of the ore, regulations pertaining to local environment and many other factors.
To begin a mining operation, it is necessary to concentrate the ore and this process is also called as beneficial. Ore needs to crush for this process. For the conversion of sulfidesto oxides, the ore can be roasted which is then later smelted to produce matte. Lastly, it undergoes a wide array of refining processes and the last process is electrolysis. For a variety of environmental as well as economic reasons, many extraction by-products are reclaimed. In extraction process, sulphuric acid is used and for this purpose sulphur dioxide gas is captured. Any process’s first stage in a metallurgical circuit treatment entails comminuting or accurate grinding. In this process, rocks are crushed thereby producing <100 μm sized small particles. Each particle will consist of ore minerals. On the basis of the ores being sulfide or oxide, copper liberation process will depend.
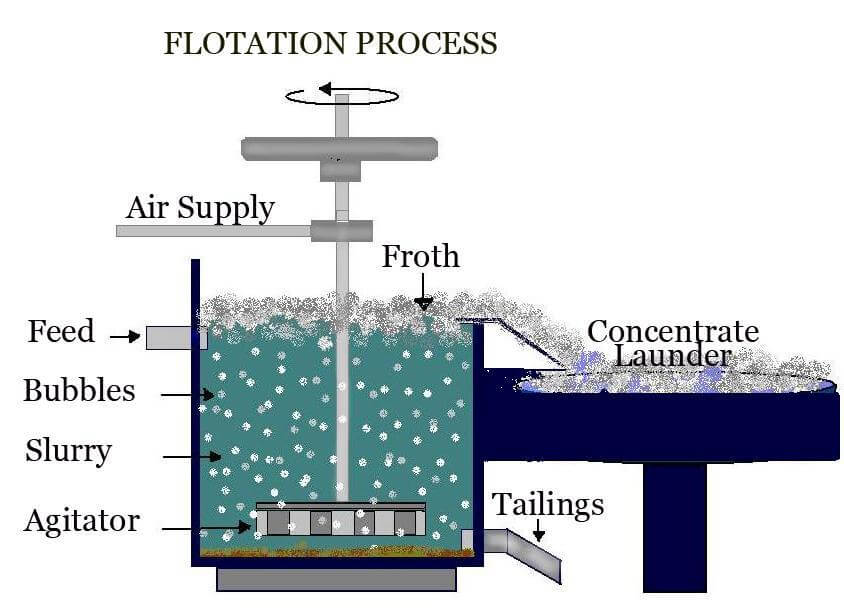
Any steps that are taken to extract Copper Wire from the ore will depend on its nature. Normally, hydrometallurgical liberation procedure is undertaken for the oxide ores. In this process, the property of ore minerals solubility is used. Froth floatation technique is used in primary that is un-weathered and secondary that is supergene sulphide ores to separate gangue from ore. Using simple gravity circuit, the mineral can be recovered from local copper with ore bodies that are rich in supergen copper.
Crushing of grounding copper ore is done in such a manner that between gangue and copper sulfide mineral ore, high degree liberation may occur. At this time the ore is wet and mixed with xanthates and is suspended in slurry. This process offers sulfide particles-hydrophobic. The ore after being treated is entered into an aeration tank filled with water that contains surfactant like methylisobutyl carbinol (MIBC). In the slurry, air is continuously forced and the air bubbles get attached to the particles of hydrophobic copper sulfide. These particles are conducted to the surface where froth is formed that is later skimmed off. A cleaner scavenger cell is used for these skimmings and excess silicates are removed. The quality of concentrate can be negatively impacted by sulfide minerals hence it is necessary to remove them.
After all these procedures, final concentrate is then sent for smelting. The rock that has been left behind in the flotation cell is either sent for further processing or discarded. Process efficiency is improved by using lime that helps in raising pH level of water bath. It causes the collector ionizing more. In both zone materials, iron exists. This way, a variety of procedures can be used to extract copper from the ores.